Comparison of Isolation Transformer Vs Autotransformer: Ultimate Pro's Guide
Jan 20,2025 | nretec
Introduction
In electrical engineering, choosing the right transformer is crucial for equipment safety and functionality. This comprehensive guide explores why isolation transformers often prove superior to autotransformers and provides essential insights for selecting the most suitable transformer for your specific needs.
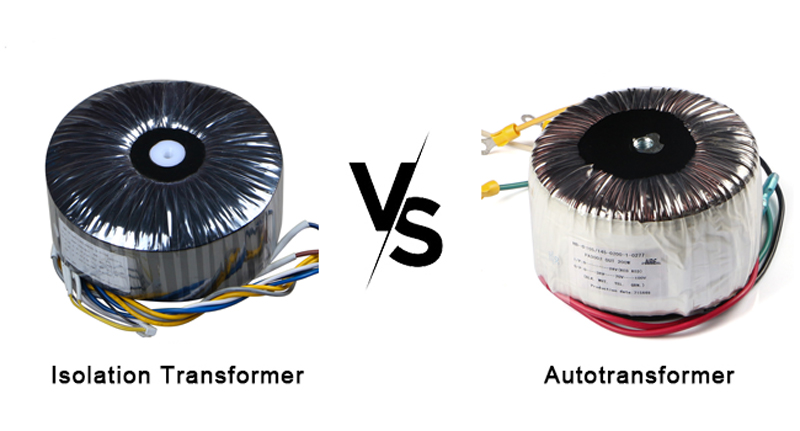

Advantages of Isolation Transformer
1. Enhanced Safety Features
The primary advantage of isolation transformers lies in their complete electrical isolation. With no direct electrical connection between primary and secondary windings, they provide superior protection against electrical shocks and system failures.

2. Superior Interference Rejection
- Effective blocking of common mode noise
- Significant reduction in electromagnetic interference
- More stable output voltage delivery
3. Advanced Grounding Protection
Isolation transformers enable the creation of separate grounding systems, which is essential for:
- Protection of sensitive equipment
- Elimination of ground loop currents
- Enhanced system stability
Primary Applications
Isolation transformers are particularly valuable in:
- Medical Equipment and Facilities
- Precision Testing and Measurement Instruments
- Professional Audio Equipment
- Laboratory and Research Equipment
![]()
![]()
Selection Guidelines
While isolation transformers typically command a higher price point, they are strongly recommended for:
- Applications requiring maximum safety standards
- High-end electronic equipment
- EMI-sensitive devices (instruments, sensors, etc.)
Conclusion
Despite their higher initial cost, isolation transformers offer superior value through enhanced safety, interference protection, and equipment longevity. The selection between isolation transformers and autotransformers should be based on:
- Specific application requirements
- Safety standards and regulations
- Budget considerations balanced against long-term benefits
- Environmental and operational conditions